Healthy liver performs many functions, such as converting nutrients and drugs absorbed from the digestive tract into ready-to-use chemicals and removing toxins and other chemical waste products from the blood. Health would be damaged by liver cancer. Primary liver cancer is cancer that forms in the tissues of the liver. Secondary liver cancer is cancer that spreads to the liver from another part of the body.
The number of people suffering from liver cancer is on the rise and statistics issued by National Cancer Institute is that there are 33,190 new cases and 23,000 deaths from liver and intrahepatic bile duct cancer in the United States in 2014. According to the American Cancer Society, the relative 5-year survival rate from liver cancer is about 15% indicating the liver cancer treatment need to be explored and improved.
Prof.
ZHANG Huafeng, Prof.
GAO Ping and members of their team together found a HIF-1 inhibition promotes cancer progression, which is important for liver cancer clinical research and raise hope for liver cancer patients. The findings will provide opportunities to design novel therapeutic strategies to harness human malignancies, which was entitled “
HIF-1-Mediated Suppression of Acyl-CoA Dehydrogenases and Fatty Acid Oxidation Is Critical forCancer Progression” in
Cell Reports on Sept 25.
The reprogramming of cellular energy metabolism is one of the recognized ‘‘emerging hallmarks’’ of human cancer. In cancer cells, the conversion level of glucose to lactate is higher than that of normal cells. AS cell fate is determined by the metabolism, plenty effort has been spared into understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying its reprogramming in cancer cell. For instance, hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1) mediates a metabolic switch that shunts glucose metabolites away from the mitochondria, associating with generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and cell death.
Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1) mediates a metabolic switch that blocks the conversion of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA in cancer cells. Researchers reported that underthe condition of hypoxia, HIF-1 decreased reactive oxygen species levels and enhanced proliferation of cancer cells via inhibiting the medium- and long-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenases (MCAD and LCAD). Block of LCAD, not MCAD, results in the down-regulation of PTEN, a kind of tumor suppressor gene, and dramatically affects tumor growth in vivo. From the further study of mice and the 158 liver cancer samples, they identified decreased LCAD expression predicts patient mortality.
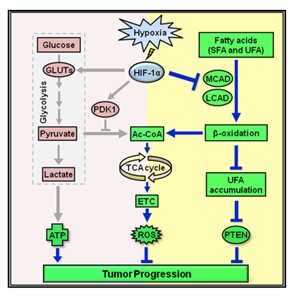
Graphical Abstract: HIF-1-Mediated Suppression of Acyl-CoA Dehydrogenases and Fatty Acid Oxidation Is Critical for Cancer Progression
(JI Jiaojiao, USTC News Center)